Mobile App Development Process: Step by Step Guide in 2026

8 December, 2025

We see hundreds of new mobile applications being launched every day, yet only a few of them gain recognition. And the reason is not the great ideas that disappear within months; it’s a mobile development process that separates successful apps from those that fade away.
As per the forecasts, mobile app downloads are going to hit 143 billion by the end of 2026, highlighting the importance of a well-structured mobile app development strategy.
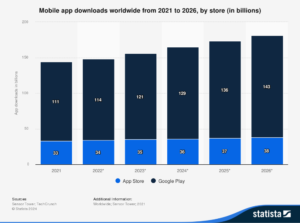
Source: Statista
With numbers like these, it’s no surprise why businesses explore top mobile app development.
Doesn’t matter if you are here to build the next global sensation or simply want to make their internal operations faster and more cost-effective. Whatever the goal is, you need a clear roadmap to get there, which this blog covers in detail.
This blog discusses the step-by-step process of creating an app in detail. It will clearly explain to you each stage with a thorough understanding.
Essential Mobile App Market Statistics
Before we discuss the stages of app development, it’s better to have a comprehensive view of mobile app development industry trends, so you can build an app that’s ready for the future.
Here are the latest insights you need to know for 2026:
- Mobile app revenue is projected to exceed $633 billion by the end of 2026.
- The Apple App Store currently offers about 96 million apps.
- The Google Play Store has around 87 million apps available.
- In 2026, the average mobile user spends 6 hours a day inside apps.
Without further ado, let’s get into the main section.
8 Key Stages of Mobile App Development: Follow Step-by-Step
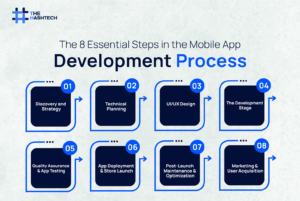
Each stage plays an important role in shaping how your app performs in the real business world. Here are the key stages of mobile app development that you need to take into account for successful development.
Step 1 – Discovery and Strategy
The establishment of an entire app development process depends on defining the app strategy. It is the initial stage where you begin brainstorming about your future app, its primary objective, capabilities, audience, and business model.
Identifying the Objective
Every successful app starts with a real need, whether it’s for simplifying the task, saving time, or making the communication smooth. So, it’s important to clearly understand the problem your app is meant to solve.
The objective of an app can be found by answering these simple questions:
- What specific problem does your app address?
- Who is experiencing this problem the most?
- Why would users choose your app over existing solutions?
You may already have a strong idea in mind, and that’s fine. Still, writing these points down helps keep your goals clear throughout the development process. When decisions come up later, you can always refer back to this problem to make sure the app stays focused on what truly matters.
Conduct Market Analysis
Market research is the next essential step in the discovery and strategy planning of an app. This research protects you from building something that already exists, or worse, something no one wants.
As per to CB Insights, 35% of startups fail because the app doesn’t meet the market needs. To make your app an achievement, look for the gaps in the market you can fulfil.
Start by analysing competitors from these angles:
- Are there existing apps solving the same problem?
- Are people actually downloading and using it?
- How do users feel about their solution?
- What are the common frustrations or missing features?
While looking at the competitor’s apps, you can carefully evaluate:
- Feature sets
- App store reviews (especially complaints)
- UX limitations
- Monetization models
Define Target Audience
Defining the target audience means understanding exactly who the app is being built for. An app works best when it focuses on a specific group of users rather than trying to serve everyone. A clear audience helps in shaping the usability, features, and retention accordingly.
You can define your target audience by:
- Demographics: age, role, location
- Behavior: device usage, technical comfort level
- Expectations: performance, privacy, design quality
For example, an app designed for startup founders will have very different needs compared to one built for field workers. Clarifying this early ensures the app fits the people who will use it daily.
Feeling overwhelmed by technical choices?
Our experts can help you define the right architecture and features for a scalable, successful app.
Stage 2 –Technical Planning
After your idea is validated, the market research is done, and the audience you are building an app for is decided, then move towards the technical planning. In this stage, you have to be practical about how the app will be built and maintained.
Choose the Right App Type
There are four major app development types: Native, Cross-platform, Hybrid, and Progressive Web Apps (PWA). You have to choose the right app architecture according to the performance needs, budgets, and future scalability your app requires.
If you want a deeper look at frameworks, tools, and stacks used today, you may find our guide on Top Technologies for Creating Mobile Apps You Should Know helpful.
- Native Apps are built for a single platform (iOS or Android) to deliver the fastest performance.
- Cross-Platform Apps use a single codebase to run on both platforms, and are often budget-friendly.
- Hybrid Apps are a Web-based app wrapped in a native shell, developed faster.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWA) are highly responsive websites that function like apps through a browser.
We will compare these in detail later, but for now, the decision should support your core goals.
According to recent data from Statista, native development remains the gold standard for industries where speed and security are non-negotiable. For instance, if you are building a fintech app or healthcare app, going native is the best way to ensure your platform is fast and compliant.
Pick the Right Platform (iOS, Android, or Both)
The next step in technical planning is picking the right platform. Whether you want an app for Android, iOS, or both will have an impact on its development cost, timelines, feature availability, and how quickly the app reaches its users.
To make the platform choice easier, you need to clearly understand how and where users will actually use the app. And for that, you can consider going through this comparison:
| Platform | When It Makes Sense | Key Considerations |
| iOS | Targeting premium users or monetization-driven apps | Higher spending users, strong design standards |
| Android | Reaching a broad, global audience | Larger market share, device variety |
| Both (iOS + Android) | Building scalable, growth-focused products | Higher cost, wider reach, future-ready |
Define Core Features in App
Your core features are the ‘must-haves’ that make your app actually work. Many projects fail because they try to solve too many problems at once, leading to a cluttered experience that’s difficult to maintain. By starting with a focused set of features, you can launch faster and give your users exactly what they need.
Every feature should answer one simple question: Does this help the user solve the primary problem better? If the answer is unclear, it’s likely not a core feature.
A practical way to approach this is to separate features into priority levels:
- Must-have features are essential for the app to function and deliver its promise.
- Nice-to-have features can be added later without affecting usability.
- Future features support long-term growth but are not needed for the first release.
This strategy aligns with many successful mobile application development tips, as features can be rolled out based on real user feedback.
For a comprehensive list of innovative features to consider, explore our guide: [Top 25 Mobile App Features to Make Your App Stand Out].
Take Project Estimates
Estimation is usually done after the platform and core features are finalized, as these directly influence the cost involved in development. Without a realistic estimate, many apps stall midway due to budget overruns and never make it to launch.
For a precise project estimation, you should be clear with:
- The approximate budget needed to build and launch the app
- Type of specialists required at each stage of development
- Practical timeline for completing and releasing the product
With this cost estimation, you can move forward to a development plan that’s actually sustainable.
For a deeper dive into budgeting, see our detailed breakdown: [How Much Does It Cost to Create an App in 2026? A Complete Guide].
Create a Product Roadmap & Timeline
How long your app will take to develop is the next thing we plan. If you are working with professional app developers, you can ask them to organize the work into clear phases and milestones so you can see the progress step-by-step.
A roadmap usually includes:
- Initial release (MVP or first version)
- Short-term improvements based on feedback
- Long-term features aligned with growth goals
This roadmap ensures smoother execution across all app development steps.
Got a great app idea?
Let’s validate it together. A 30-minute strategy session can save you months of development.
Stage 3 –UI/UX Design
For users, the design is the product. No matter how strong the technology behind an app is, people judge it within seconds based on how easy it feels to use. If screens feel cluttered, navigation is confusing, or actions don’t behave as expected, users don’t try to figure it out. They leave.
According to Google’s UX research, users are up to 88% less likely to return to a product after a poor experience. This is why UI/UX design deserves deliberate time and structure.
In this stage, we are going to look at each of the design areas more closely.
Map User Workflows
Before you move on to designing the screens, you need clarity on what information exists inside the app and how users should access it. This is where information architecture comes in.
Information architecture defines:
- What data the app contains
- How that data is grouped and prioritized
- How users move between different sections
As you get clear on this, user workflows are mapped. In the workflow, you have to outline all possible actions a user might take, from signing up to placing an order and making a transaction. The clearer these paths are in the app, the easier navigation becomes for users.
Wireframes
Wireframes are simple, low-detail representations of screens that focus on placement rather than appearance. At this point, decisions are made about where content lives, how users navigate, and which actions deserve the most attention.
Because wireframes avoid colors, branding, and visual styling, they keep discussions focused on usability rather than aesthetics. This makes it easier to remove friction and refine flows before committing to detailed designs.
Style Foundations
In the next UI/UX design step, you have to care about the factors that define your visual identity. It includes typography, color usage, spacing, and component behavior. These are the core design elements for style:
- Typography
- Color palette
- Spacing and layout rules
- Button styles
- Widget designs
- Any other important UI components
Deciding on these helps you maintain consistency within your app.
High-Fidelity Mockups
Once your style foundations are ready, the next step is creating mockups. These are the final high-fidelity visuals produced by applying your brand’s colors, fonts, and icons to the initial wireframes.
The primary task is to make sure that every button, menu, and screen remains consistent throughout the entire platform.
Interactive Prototypes
Prototypes are the last stage of UI/UX design where we connect screens into a working experience. Instead of static images, users can tap, swipe, and move through as if the app were live. This is one of the most valuable stages of UI/UX design because it reveals issues that static designs cannot.
Prototyping allows you to:
- Test onboarding clarity
- Validate task completion flows
- Identify confusion before development
Catching usability issues here saves significant time and cost later, when changes would otherwise require code rewrites.
Stage 4 – The Development Stage
Now is the time to work on one of the most important stages of mobile app creation. This stage includes working on the following components:
Backend Development
In the backend stage of development, the focus is on managing the server-side implementation, which has a direct impact on the app’s performance.
It begins with choosing the appropriate programming languages based on your app’s requirements, and moving forward to coding. The development team you choose will also establish the database structure (where your data will be stored) and the hosting environment to work in.
The backend phase is a critical stage in the mobile development process. The decisions made here directly define how well your app can scale and perform in the future.
If you want a backend as strong as other competitive apps, partnering with an experienced software development company is a critical choice. Their guidance through all development phases will result in your system being robust and designed to expand with your growing audience.
Frontend Development
The frontend of a mobile app is what your end user sees and interacts with, such as screens, buttons, animations, and transitions.
At this point, developers convert approved UI/UX designs into real interfaces. Every tap, swipe, and screen transition is carefully implemented to feel natural. Because even a beautifully designed app fails if screens load slowly or interactions feel laggy.
You also decide how the frontend is built based on your platform choice. In native mobile app development, interfaces are optimized specifically for iOS or Android. In cross-platform development, frameworks like Flutter help maintain consistency across devices while saving development time.
Integration of Third-Party Services
Very few apps today are built entirely from scratch. Instead, they rely on trusted third-party services to deliver essential functionality quickly and securely.
During development, you integrate third-party tools like payments, push notifications, analytics, and user authentication. With the help of these integrated features, you can enhance the overall experience of the app.
However, these integrations must be handled carefully. Each service needs to be configured correctly so it doesn’t slow down your app or create security risks. For example, payment integrations must follow strict compliance standards so that no data breach happens.
DevOps Implementation
DevOps implementation is driven by the need to improve software reliability. By bringing software development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams to work in sync, DevOps makes it easier to meet user needs faster and execute technical goals without any delays.
The key practices within a DevOps framework include:
- Automating the process of building and delivering code to keep updates fast.
- Applying encryption to protect information, whether it is being moved or stored.
- Controlling who can see or change specific parts of the system to prevent unauthorized access.
- Setting up automated checks to ensure the app follows legal privacy standards like GDPR.
Ultimately, DevOps protects your app’s reliability and your peace of mind by ensuring that development and operations are perfectly in sync long after the initial launch.
Ready to start building?
With many years of experience, The Hashtech knows how to build powerful apps and we can build yours too.
Stage 5 – Quality Assurance & App Testing
As soon as your app is developed, you need to ensure your app’s quality is optimal. With the specialized quality assurance and software testing in place, you catch bugs early and ensure a smooth experience for your users.
If you want to ensure a high-quality app release, these are the four most important testing stages you have to undergo:
Functional Testing
Functional testing verifies that every feature in your app works as intended. This is where you step into the user’s shoes and test complete workflows rather than isolated actions.
You validate whether users can easily:
- Sign up and log in
- Search and filter
- Upload files
- Process payment
- Edit profile
- Error handling
- Share content
If a button doesn’t respond, data doesn’t save, or a flow breaks midway, users lose confidence immediately. Functional testing protects your app from these trust-breaking moments and is one of the most important app development steps before launch.
Performance Testing
Performance testing focuses on how your app behaves under pressure. An app that works perfectly during development can slow down or crash once real users start using it simultaneously.
At this stage, you test how your app performs when:
- Multiple users are active at the same time
- Network conditions are poor or unstable
- APIs respond more slowly than expected
According to Google, apps that take longer than three seconds to load experience significantly higher abandonment rates.
Usability Testing
The usability testing often reveals the problems that internal teams overlook. For the usability testing, you have to observe:
- Where users hesitate
- Which labels confuse them
- Which actions feel unintuitive
With the right usability testing, you can identify whether users can navigate your app intuitively without instructions.
Security & Compliance Testing
If your app is going to handle the personal user information, payments, or location data, this step is non-negotiable. The stage of security testing includes focusing on factors like data encryption, secure authentication, and vulnerability assessment. Because most security issues happen due to weak passwords, or ignoring important privacy rules like GDPR or CCPA.
That’s why security shouldn’t be something you add at the end; it needs to be part of every step in your app development life cycle.
Device & OS Compatibility Testing
Your users will access your app on different devices, screen sizes, and operating system versions. Despite how or where the app is used, compatibility testing helps in making sure the app is consistent.
This step is especially important in Android development due to the number of devices out there. Without compatibility testing, you risk a broken experience for many users, which can alienate a huge part of your audience right at launch.
Stage 6 – App Deployment & Store Launch
You are now finally ready to deploy your app. But before you do that, it’s better to go through different distribution methods based on the platform your app is built for.
Preparing for App Store & Play Store Submission
In most cases, you will either publish your app on the Apple App Store, Google Play Store, or use a private distribution option. See the few most important factors while preparing an app for submission:
- Complete accurate metadata
- Real unmodified screenshots
- Public privacy policy URL
- Working demo account credentials
- All finished content inside
- App store compliance
- Correct age ratings
Both Apple and Google have strict submission requirements. Even small mistakes, such as missing privacy disclosures or incorrect metadata, can delay approval.
App Store Optimization (ASO) Basics
You might also be thinking about how to make your app easier for users to discover. This is where App Store Optimization (ASO) comes in. ASO tools help you improve your keywords, study user feedback, run A/B tests, optimize search ads, and more. All of this boosts your visibility and ranking in app store searches.
Beta Release Strategy
With a beta release, you can test your app with real users before a full launch. This controlled rollout helps identify issues that internal testing might miss.
Stage 7 – Post-Launch Maintenance & Optimization
After your app is launched and users start downloading it, the next big step is to watch how it performs. This phase is extremely important, sometimes even more time-consuming than building the app, and it has to be handled continuously.
Here are some key metrics you should keep an eye on:
- Total downloads
- Daily and monthly active users
- Average session duration
- Retention rate
- Churn rate
- Conversion rate
- Customer lifetime value (CLV)
- User ratings
- User reviews
Along with these numbers, you should also monitor app crashes, performance issues, bugs, and user support requests. This helps you improve the app over time and keep it running smoothly.
Remember, the work isn’t finished when your app goes live. This is actually when the real journey begins.
Mobile apps need frequent updates to stay compatible with new OS versions, store policies, and performance requirements. Without regular maintenance, your app may stop working properly and lose users.
So, always plan for ongoing support. You can manage it yourself or rely on an external team it depends on what works best for you.
If you partner with a mobile app development company, they will usually provide post-launch maintenance services, making it easier for you to keep everything updated without extra hassle.
Stage 8 – Marketing & User Acquisition
Completing development is a milestone, but the truth is, you are still one step away from making your app top-ranked. In this phase, your focus is on making sure the right audience discovers your app, installs and uses it.
So, if you want to hit those top-rated rankings, you need a marketing plan that keeps your product in front of the right people. Here’s how to make that happen.
Pre-Launch Marketing Strategy (Paid & Organic App Promotion Channels)
At this stage, you have to position your app for market visibility. This includes defining who the app is for and what problem it solves better than existing alternatives. With this clarity, you can better target the audience and convey the core message.
You should start by creating a simple landing page that explains your app’s purpose and captures early interest through sign-ups. At the same time, prepare the descriptions, screenshots, and preview videos on the app store so that users immediately understand the value when they encounter your app.
Paid & Organic App Promotion Channels
The next great thing you can do is use organic and paid channels to reach users where they already spend time.
For organic growth, prioritize:
- App Store Optimization (ASO) using relevant keywords and clear descriptions
- Social media and content marketing to build long-term trust
- Referral or invite programs that encourage sharing
For paid promotion, start small and test:
- App install ads on search engines and social platforms
- Audience targeting based on behavior and intent
- Campaign performance based on engagement, not just install
Retention & Engagement Strategies
After users install your app, your priority is to keep them engaged. This starts with onboarding. You should guide users through key features step by step, helping them experience value as quickly as possible. The faster users understand how your app helps them, the more likely they are to stay.
Use in-app messages and push notifications thoughtfully. Also, track where users drop off, which features are most used, and what drives repeat usage. These insights help you to improve based on the real user needs.
Now that you have a solid understanding of the app development process, let’s explore the four primary approaches to creating a mobile application. This will help you determine the best way to bring your app to life.
Native, Hybrid, Cross-Platform, or PWA: Which Mobile App Development Path Should You Choose?
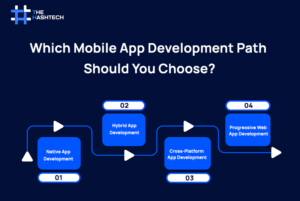
The mobile app development life cycle is carried out with four different paths, each of which comes with its own benefits and drawbacks. For making the right choice, you must have absolute clarity on your business goals, target audience, budget, and timeline.
The mobile app development framework you select directly affects your app’s performance. So, here is an in-depth analysis of each of the options:
1. Native App Development
Native app development is an app made specifically for one operating system. It uses the platform-specific programming languages like Swift or Objective-C for iOS, and Kotlin or Java for Android.
For example, a banking app built natively for iOS can use Face ID for login, while on Android, a native version can use fingerprint authentication. These features work smoothly because the app is built specifically for each platform.
Best For:
If you are building an app where high-end graphics or offline access are vital to the experience, Native is the way to go. This is why it is the standard for high-action gaming app development.
Pros
- Best performance and speed
- Full device feature access
- Most secure and reliable
- Natural platform feel
Cons
- Two apps, higher cost
- Longer development time
- Two separate code teams
2. Cross-Platform App Development
Cross platform app development allows developers to build an app for multiple platforms. Whether it’s an Android app development or an iOS app development, a single code is enough to make an app for both.
Technologies and frameworks like Xarmin, Flutter, and React Native have been used for this purpose. With the shared layouts, functionality, and navigational patterns, it is easier to provide a consistent experience to the users.
Best For:
A cross-platform app is a perfect choice for businesses with limited budgets and timelines. They work well for social apps, content apps, e-commerce platforms, and MVPs where rapid iteration is important.
Pros:
- One code, both platforms
- Faster and cheaper build
- Same design everywhere
- Fast update rollout
Cons:
- Slightly slower performance
- Complex features harder
- Different platform bugs
3. Hybrid App Development
Hybrid app development is a combination of web technologies with native app functionality. These apps are created using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which run on multiple platforms using a single codebase.
Through using plugins, hybrid apps can access certain device features like the camera or GPS. And it offers a much faster development process than building separate native apps.
Best For:
Hybrid apps are suitable for content-heavy applications where performance is less critical. Examples include blogs, news portals, or internal enterprise apps that need quick deployment on multiple devices.
Pros:
- One simple web codebase
- Very fast to update
- Lowest upfront cost
Cons:
- Slow, laggy performance
- Limited hardware features
- Feels like website
4. Progressive Web App (PWA) Development
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) function like native apps but run through a web browser. Built using standard languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, they offer a single, cost-effective codebase that works across all platforms.
These apps provide a smooth user experience by supporting home screen installation, offline access, and push notifications. This is what makes them an increasingly popular choice for mobile solutions.
Best For:
PWAs are best for businesses seeking accessible and lightweight apps. They work well for marketplaces, service bookings, and informational apps targeting users in areas with limited storage or connectivity.
Pros:
- One link, all devices
- Instant updates, no approval
- Works without installation
Cons:
- Few phone features work
- Hard to find in stores
- Slower for complex tasks
Looking to Build Your Mobile App Development Process?
Building a mobile app development project takes planning, teamwork, and the right skill set. Doing it on your own can feel overwhelming but having an experienced partner makes the whole journey smoother.
If you have an app idea but don’t know where to begin, our team at The Hashtech is ready to guide you.
We handle every part of the mobile app development process from shaping the strategy to designing, launching, and monetizing your product.
Our experts have worked with many industries, including eCommerce, healthcare, transport, food services, fintech, and real estate.
As a trusted mobile app development company, we build digital solutions that solve real user challenges, bring value to businesses, and support long-term growth.
Ready to transform your app idea into a polished product?
From strategy to launch and beyond, our team provides the expertise to make it a success.
FAQs Related to the App Development Process!
How To Build an App For My Business?
Building an app for your business starts with an analysis of the requirements. It helps in identifying your challenges, competitors, and the core problems your app solves. After giving a comprehensive view of this, you have to follow up with planning, UI/UX designing, development, testing, and ongoing maintenance to make it a successful release.
What is the life cycle of an app?
The app life cycle is the complete journey of a software application, from its initial idea to its eventual retirement from the market.
This lifecycle is carried through six different phases, including development, introduction (launch), growth (user acquisition), maturity (peak usage), saturation (market competition), and decline.
What is the timeline for app development?
The mobile app development timeline depends on how advanced your app is. A standard or mid-level app usually takes around 2–3 months to build. However, if your app includes many features or complex functionality, the development process can extend to 6 months or even up to a year.
What Does A Mobile App Developer Do?
A mobile app developer writes the code that turns your ideas into a fully functional app. They work on either the front-end (what users see and interact with) or the back-end (server, database, and application logic), ensuring the app is useful with the technical plan.
What are the 5 phases of the app development process?
The common framework that breaks the app development process into 5 phases:
- Research and Planning:Defining strategy, scope, and requirements.
- Design:Creating wireframes, prototypes, and the final user interface (UI/UX).
- Development:The actual coding for the app.
- Testing and Quality Assurance:Rigorously checking for bugs and usability issues.
- Deployment and Maintenance:Launching the app on stores and providing updates and support.
How much does it cost to build a mobile app?
The cost to build a mobile app ranges between $20,000 to over $350,000. The final price depends on key factors like app complexity (simple, mid-tier, complex), the development region (rates differ by country), the team structure (agency vs. freelancers), and the chosen platform (Native, Cross-Platform, etc.).
What are the 3 types of apps?
The mobile app is divided into three main categories that are Native, Hybrid, and Web apps.
- Native Appsare built specifically for one operating system, like iOS or Android, using languages such as Swift or Kotlin.
- Hybrid Appsare built using web technologies like HTML5 and JavaScript, but are wrapped in a native container.
- Web Appsare essentially mobile-optimized websites that users access through a browser.